Is Keto Healthy? Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis
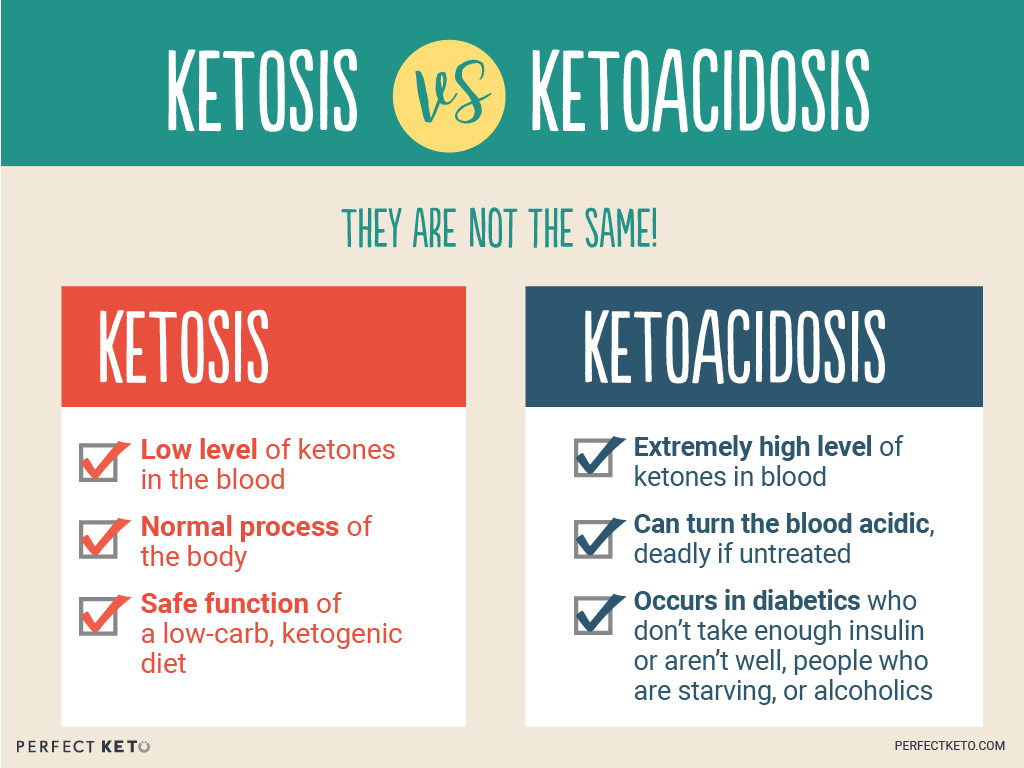
Ketosis vs. ketoacidosis — are they the same thing?
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate diet where you try to enter a state of ketosis — a natural state where you burn fat, rather than carbs, as your primary energy source. As the keto diet rises in popularity, ketosis often gets confused with ketoacidosis — a diabetic complication which is very serious, even life-threatening.
When it comes to ketosis vs. ketoacidosis, these are two very different states. However, there is plenty of confusion between the two. To clear up any misconceptions — and help you understand ketosis a bit better — you’ll learn about both metabolic states in this guide.
An Overview of Ketosis
A ketogenic diet (keto, diet) is centered around the process of ketosis. Before explaining the difference between ketosis vs. ketoacidosis, it’s important to understand ketosis.
Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body switches to burning fat for energy, rather than carbohydrates. Burning carbohydrates (glucose) for energy is the default function of the body, so if glucose is available, the body will use that first[*].
How the Keto Diet Helps You Enter Ketosis
During ketosis, the body transitions to burning ketones instead of glucose. This is a survival adaptation by the body for handling periods of famine or fasting, extreme exercise, or anything that “starves” the body of body of carbs or sugar.
Keto dieters try to mimic this process by purposely limiting their carb intake, thereby using up their excess glycogen (glucose) stores.
Those following the diet restrict their carbohydrate intake from 20–50 grams of carbs per day, while increasing their fat intake exponentially. When no glucose is present, the body will adapt and burn fat stores, or ketones, for energy instead[*].
During ketosis, ketone bodies are created by the liver from fatty acids. These ketones are then used by the body to power all of its biggest organs, including the brain[*].
Studies show ketosis has a number of health benefits, which you’ll learn about below.
Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis: What’s the Difference?
As you just learned, nutritional ketosis is a safe, natural process sparked by the keto diet. Ketoacidosis, on the other hand, is a dangerous metabolic state commonly seen in people with type 1 diabetes (and sometimes, with type 2 diabetes).
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Ketoacidosis is a condition where people with diabetes produce dangerously high levels of ketone bodies. This happens when the body can’t produce enough insulin.
Without enough insulin present, the body breaks down fat as fuel, causing a high level of buildup of ketones in the blood that will “spill over” into the urine. This buildup causes the blood to turn acidic[*]. With DKA, the amount of ketones in the body can be 3–5 times greater than would be necessary to enter ketosis.
Risk Factors of Ketoacidosis
Poor diabetes management is one of the main causes of DKA (for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes), including not getting enough or using the correct insulin doses. DKA is also often the first sign that someone has diabetes. If you do have diabetes or at risk for developing it, be sure to always follow the blood sugar management and insulin therapy your healthcare provider.
Other possible triggers for DKA include[*]:
- Starvation combined with alcoholism
- An overactive thyroid
- Alcoholism
- Acute major diseases like pancreatitis, sepsis, or myocardial infarction
- Illness or infections like urinary tract infections and pneumonia
- Medications that may inhibit proper use of insulin
- Drug abuse
- Stress
- Heart attack
Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis should be handled by your doctor. However, before things get to that point, you should know the warning signs of DKA.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is associated with a number of negative side effects, and symptoms can develop in as little as 24 hours. DKA often involves some of the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- High blood glucose levels (high blood sugar levels)
- Dehydration
- Excessive thirst or dry mouth
- Hyperglycemia
- Vomiting
- Nausea or abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath or gasping
- Fruity odor or bad breath
- Feeling overly tired
- Feeling confused
Those with diabetes should use caution if they experience any of the triggers above and should see their doctor immediately — or even go to the emergency room — if they have any of the symptoms of DKA.
However, nutritional ketosis while eating a well-balanced keto diet should only produce low levels of ketones that are safe for the average person and not a cause for concern.
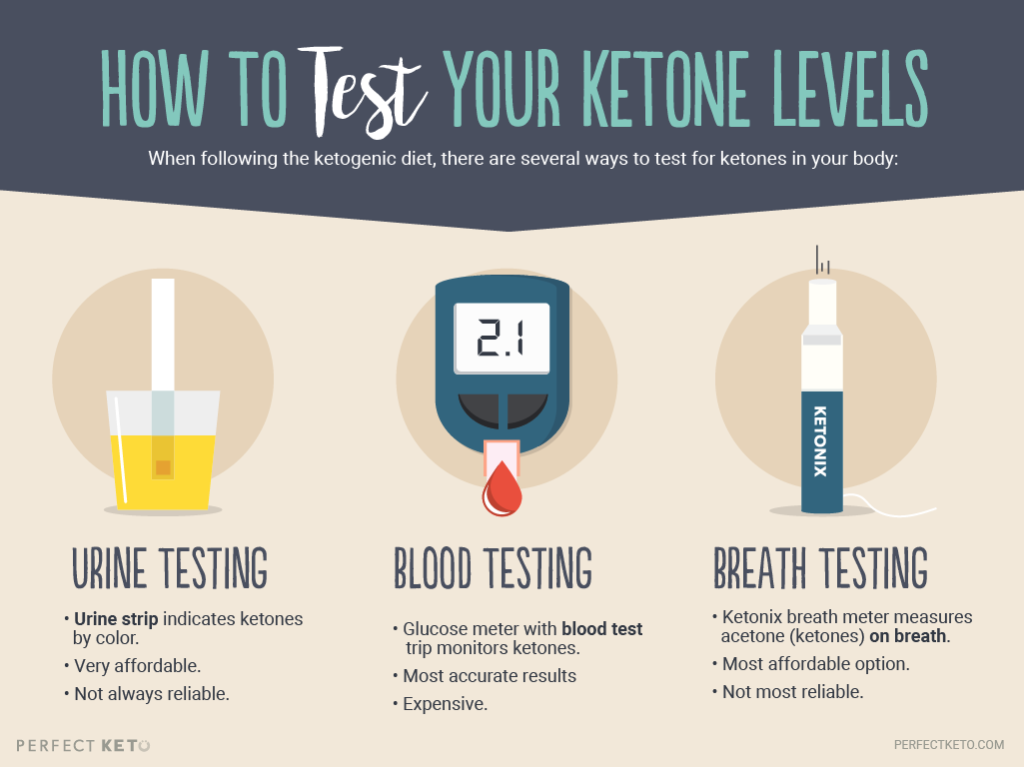
Knowing If You’re in Ketosis: Test Your Ketone Levels
The best way to determine whether you’re in ketosis, and if the level of ketones in your body is healthy, is to test your ketone levels. When you’re in ketosis, ketones that aren’t used will spill over into different areas of the body: the breath, urine, and blood.
Blood ketone levels can range from zero to very high, and measuring them regularly can give you a good understanding of where you are in ketosis. Levels are measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L) and the general ranges include:
- Less than 0.6 mmol: negative ketone level
- Between 0.6 and 1.5 mmol: low to moderate ketone level
- Between 1.6 and 3.0 mmol: high ketone level
- Greater than 3.0 mmol: very high ketone level
Anything between 0.6 and 3.0 mmol is usually optimal ketone range for someone on a keto diet. Ketone levels during diabetic ketoacidosis are 3–5 times higher than the healthy ranges for nutritional ketosis.
Related: 10 Signs You’ve Entered Into Ketosis
Types of Ketone Tests
There are three main types of ketone tests you can do at home to monitor the levels of ketones in the body.
Urine Testing
Ketone urine tests are a quick, simple, and affordable option. Using specific urine strips you can find online, your ketone level is indicated by color after peeing on each strip.
The downside to this method is that many keto test strips are unreliable. To ensure you’re getting the most accurate reading possible, use Perfect Keto Ketone Testing Strips.
Blood Testing
In contrast with urine testing, blood tests for ketone levels are very accurate. Using a blood glucose meter and a test strip, you draw a small amount of blood for measurement.
If you’re going to use this method to test often, be warned that it can be pricey. Each test strip can cost between $5 and $10 dollars, which adds up.
Breath Testing
Measuring ketones on the breath is not the most reliable method, but it’s helpful when used with other methods. Breath tests take place using a Ketonix breath meter to test the amount of ketones present on your breath.
The advantage of this method is that once you purchase the meter, there are no extra costs involved with repeated tests.
Health Benefits of a Keto Diet
Unlike ketoacidosis, ketosis is not harmful for your body. In fact, ketosis can provide a number of health benefits, including the following:
It Can Help You Lose Weight
The keto diet has been shown to bring better weight loss results than calorie restriction[*]. This is likely due to the fact that those on a keto diet are burning stored fat for energy.
Those on the keto diet often experience fewer hunger pangs and cravings, due to the high satiety of of a high-fat diet. Those in ketosis typically experience appetite suppression, aiding in weight loss[*].
It Can Help Improve Insulin Levels
Unlike ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening to those with diabetes, ketosis can actually help improve insulin levels in those with diabetes. In one study performed on obese people with type 2 diabetes, they ate a normal, Standard American Diet for one week before switching to a low-carb, high-fat diet for two weeks.
The result? The individuals saw a 75% increase in insulin sensitivity. Plus, they consumed 30% fewer calories, which could have been due to appetite suppression[*].
It May Boost Brain Health
Ketosis has been shown to help reduce seizures in people with epilepsy, especially kids[*]. It may also have benefits for people with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or other degenerative cognitive diseases due to the neuroprotective impact of ketones have on the brain[*].
Learn More: Keto and Alzheimer’s: How Ketones Impact Brain Health and Function
There is some evidence suggesting that a keto diet can have benefits for productivity and mental performance, as well as improving memory and mild cognitive impairment[*][*][*].
It Could Help Improve Physical Performance
Athletes, weightlifters, and regular weekend warriors trust the keto diet to boost their performance at the gym. First, the keto diet helps improve body composition (not just weight loss), which helps to preserve muscle mass[*].
Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis: One Benefits Your Health, the Other Harms It
As you have learned, ketosis vs. ketoacidosis are two starkly different metabolic states. Nutritional ketosis is a natural process where your body burns fat, rather than glucose for fuel. When you enter ketosis, your body can experience a number of health benefits, such as mental clarity, improved insulin levels, and better results at the gym.
Ketoacidosis, on the other hand, is a dangerous byproduct for those with type 1 diabetes. With ketoacidosis, ketone levels in the blood reach levels 3–5 times higher than is necessary to reach ketosis. At such high levels, the blood becomes acidic. By sharp contrast, ketosis has been shown to actually decrease insulin resistance within diabetic patients.
It’s important to understand ketosis vs. ketoacidosis. If you’re curious about your ketone levels, you should test them. Order Perfect Keto test strips to ensure your ketone levels are at healthy levels.


