Thinking about keto? You’ve probably heard about some of the amazing results people have gotten from the keto diet, or seen it for yourself in a family member, friend, or coworker.
Keto is a low-carb diet that’s particularly helpful for people who are trying to lose weight or improve their metabolic health. It can help you burn stored fat, improve your blood sugar levels, and get your appetite under control. Keto may even offer some brain health benefits, too.
In this guide, we’ll share what you need to know about the keto diet for beginners — including what to eat and what to avoid, how to get started, and a three-day sample keto diet plan.
What Is the Ketogenic Diet?
Keto is a low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein eating pattern. Carbs, fat, and protein are micronutrients, or the components of food that provide calories. Generally, most people on keto aim for this macro breakdown:
- Carbs: 5% of calories or less
- Protein: 20-25% of calories
- Fat: 70-75% of calories
For many people, this works out to about 25-50 grams of carbs per day.
Carbs — things like bread, pasta, potatoes, sugary sodas, and even fruit — break down in the body into sugars and have a large impact on your blood sugar levels.
Although protein and fat can also affect your blood sugar levels, they have much less impact than carbs.
By drastically reducing your carb intake on keto, you’re able to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis. You can read more about ketosis and its benefits just below.
How Does the Ketogenic Diet Work?
The keto diet works by allowing your body to shift into a state called ketosis.
Although the body normally burns carbs for energy, in ketosis it burns fat as its primary energy source instead (*).
In ketosis, your body is able to use dietary fat or stored body fat for fuel.
Additionally, the keto diet may help reduce appetite and preserve lean muscle mass. This makes keto particularly helpful if weight loss is your goal (*).
Different Types of Ketogenic Diet
There are several different types of ketogenic diets, and they all may offer different benefits or be a better fit for certain people. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Standard: This is a regular keto diet, where you’re sticking to the same macro pattern each day and likely tracking your food intake.
- Clean: On this ketogenic diet, you’re sticking to low-carb, high-fat macro patterns, but choosing high-quality, organic foods and avoiding highly processed foods. Most people on clean keto avoid fast food, packaged snacks, artificial sweeteners, and seed oils like corn oil and soybean oil.
- Dirty: Dirty keto refers to a keto diet that is solely based on hitting your macro goals, regardless of food quality. A dirty keto diet may include things like fast food, diet soda, artificial sweeteners, and seed oils.
- Lazy: “Lazy keto” means that you’re following a keto diet without tracking your intake. This may be a good fit for you if you dislike measuring portions or tracking, but it’s easy to eat too many carbs or calories on lazy keto — which could be a problem if weight loss is your goal.
- High-Protein Keto: High protein keto is a higher-protein version of the keto diet, with 30-35% or more calories from protein (and less from fat). Protein can be very helpful for weight loss, so high-protein keto may be a good option if you’re trying to lose weight (*).
- Cyclical Keto: On cyclical keto, you follow a higher-carb diet on certain days and stick to a strict keto diet on other days. This may be particularly useful for people who have training days (during which they can eat higher carb), as well as women who want to adjust their macro intake throughout their monthly cycle for hormonal balance.
- Targeted: Targeted keto is similar to cyclical keto, but instead of adding carbs only on certain days you will add pre-workout carbs before all of your workouts. These carbs are burned up during your workout, so it’s easier to stay in ketosis (but the carbs provide an added energy and performance boost). Targeted keto is a good fit for active people.
There can be some overlap between these types, too. For instance, you may choose to follow a clean, lazy, cyclical keto diet — which just means that you choose minimally processed foods, don’t track your macros, and eat more carbs on certain days.
Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The major keto diet benefits are weight loss, brain health, and blood sugar control. Keto can be profoundly anti-inflammatory, and this anti-inflammatory effect is thought to be a major cause of the many benefits of the diet (*).
For this reason, ketogenic diets are a hot topic in the research world, and many emerging studies have found evidence to support these benefits. You can find thousands of positive stories about drastically improved health from keto online, too.
Weight Loss
Many people try keto because they want to lose weight. A quick online search will bring up thousands — if not tens of thousands — of success stories from people who have met their weight loss goals using the keto diet.
There are a few research-backed reasons that keto is great for people trying to lose weight, too:
- Fat loss: In ketosis, your body is primed to burn fat rather than carbs — so it may be easier to burn your stored body fat (*).
- Muscle sparing: Keto diets may also prevent muscle loss while you’re losing weight. This helps preserve your metabolic rate, so you’re still burning the same amount of calories while your weight decreases (*).
- Reduced appetite: Fat and protein are very filling, and many people report that their appetite is much better controlled on keto than when they are eating high-carb foods (* , *).
- Better blood sugar control: Finally, keto diets may help to stabilize your blood sugar — which could help regulate your appetite and reduce carb cravings (*).
Brain Function
Ketogenic diets have long been used effectively to help treat drug-resistant epilepsy in children (*).
Although research is still ongoing, ketosis appears to be very helpful for other aspects of brain function, too — especially for certain conditions.
Researchers have found that, in addition to epilepsy and other seizure disorders, following a keto diet may also be helpful for mood disorders like depression, mental illnesses including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, and cognitive decline (* , *).
Blood Sugar Control
Many people also try keto to help with blood sugar control. Online, you can find many stories of people who have reversed their type 2 diabetes or reached a point where they no longer need insulin or blood sugar-lowering medications thanks to keto.
Additionally, research shows that ketogenic diets can help improve blood sugar levels and insulin resistance (* , *).
Keto may be useful for type 2 diabetes, along with other conditions related to insulin resistance and blood sugar control — like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and metabolic syndrome (* , *, *).
What to Eat on a Ketogenic Diet
These foods are keto-friendly and can be part of your keto eating plan. Remember, though, to check the nutrition and ingredient labels for any packaged “keto” foods to see if they’re truly keto-friendly — it would be impossible to list all of them here.
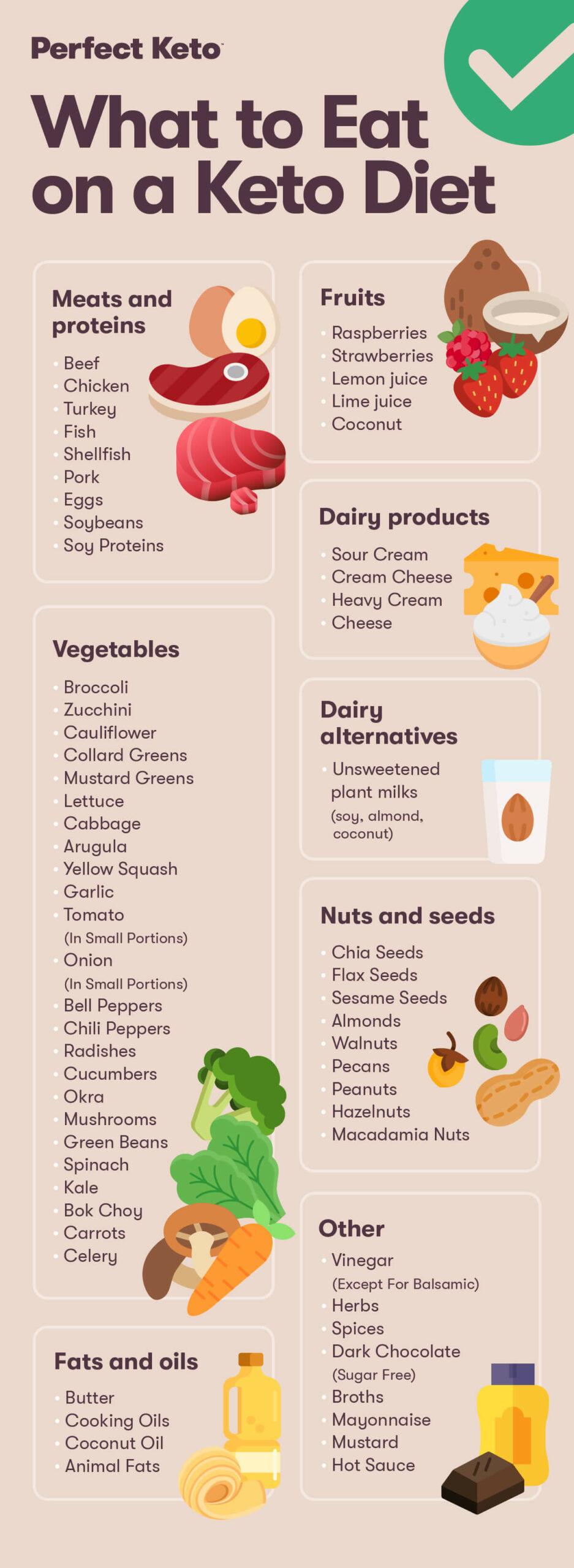
- Meats and proteins: beef, chicken, turkey, fish, shellfish, pork, eggs, soybeans, soy proteins
- Fruits: raspberries, strawberries, lemon juice, lime juice, coconut
- Vegetables: broccoli, zucchini, cauliflower, collard greens, mustard greens, lettuce, cabbage, arugula, yellow squash, garlic, tomato (in small portions), onion (in small portions), bell peppers, chili peppers, radishes, cucumbers, okra, mushrooms, green beans, spinach, kale, bok choy, carrots, celery
- Dairy products: sour cream, cream cheese, heavy cream, cheese
- Dairy alternatives: unsweetened plant milks (soy, coconut, almond)
- Nuts and seeds: chia seeds, flax seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, walnuts, pecans, peanuts, hazelnuts, macadamia nuts
- Fats and oils: butter, cooking oils, coconut oil, animal fats
- Other: vinegar (except for balsamic), herbs, spices, dark chocolate (sugar free), broths, mayonnaise, mustard, hot sauce
What Foods to Avoid on Keto
These foods are high in carbs and should be avoided on keto.

- Meats and proteins: breaded/battered meats, all beans and legumes (excepts soybeans and peanuts), imitation crabmeat
- Fruits: all fruits except for those on the keto-friendly list
- Vegetables: potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, winter squashes, peas
- Grains: bread, rice, pasta, oats, grits, flour, cornmeal, quinoa, tortillas, flatbreads, biscuits, rolls, crackers
- Nuts and seeds: cashews, pistachios
- Sugary foods: sugary soda, fruit juices, sweetened beverages, candy, cookies, cakes, snack cakes, ice cream, syrups, jellies, honey,
- Dairy products: milk, yogurt
- Other: sweetened coffee creamers, balsamic vinegar, ketchup
Remember to always check nutrition labels. There are many foods that contain more carbs than you would expect.
What Supplements Can I Take on a Ketogenic Diet?
Although you don’t necessarily need any supplements on keto, there are some that may help you thrive. Here are our recommendations:
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals that help regulate your body’s muscle function.
When you first start keto, you may experience muscle cramps, headaches, and fatigue as your body’s electrolyte concentrations shift (*).
To help prevent these unwanted side effects, supplementing with electrolytes can be a huge help.
For an easy, tasty electrolyte supplement, try Perfect Keto Daily Electrolytes.
MCT Oil
Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil is a unique type of oil with properties that make it particularly helpful for people on keto.
Some research shows that MCT oil can help deepen your ketosis, and studies have also shown that it may help your body burn more fat during exercise too (* , *).
Perfect Keto MCT Oil Powder is mess-free and ideal for mixing into protein shakes or your morning coffee.
Protein Powder
Struggling to get enough protein?
A protein powder could be a great way to up your protein intake in an easy and convenient way.
A protein shake can also be a filling on-the-go breakfast or snack, or a great way to get your post-workout protein in.
Most protein powders are keto-friendly (although you should always check the label, just in case), and Perfect Keto Whey Protein is designed for keto with added MCT oil.
Sample Keto Meal Plan
This sample three-day meal plan can give you some mealtime inspiration for your first few days on keto.
Day 1
- Breakfast: two slices of bacon and 2 eggs fried in bacon fat
- Lunch: bunless burger with cheese and roasted broccoli
- Dinner: grilled ribeye steak with sauteed mushrooms and asparagus in avocado oil
- Snack: strawberries, walnuts, and unsweetened whipped cream
Day 2
- Breakfast: protein smoothie with keto-friendly protein powder, unsweetened almond milk, ice, half an avocado, and raspberries
- Lunch: keto taco bowl with cauliflower rice, seasoned ground beef, cheese, sour cream, taco sauce, cilantro, and lime juice
- Dinner: zucchini noodle “spaghetti” with no-sugar-added spaghetti sauce and homemade meatballs (no breadcrumbs)
- Snack: hard-boiled eggs, cheese, and almonds
Day 3
- Breakfast: mushroom, spinach, and mozzarella cheese omelet
- Lunch: turkey, bacon, and avocado wrap on a low carb tortilla, with coleslaw made with no-sugar-added dressing
- Dinner: roasted salmon filet with salad (salad greens, tomato, red onion, ranch dressing)
- Snack: no-sugar-added beef jerky and baby carrots with sour cream dip
Don’t forget to check out our recipes for more inspiration.
How to Get Started with the Ketogenic Diet
Here’s how to get started on keto.

- Study up: Before you start keto, it’s important that you have a good understanding of the foundations. This article is a great start, as well as any of the other resources on the Perfect Keto blog. Be sure you have a solid idea of which foods are keto-friendly and which aren’t, as well as how to read nutrition and ingredient labels.
- Set goals and calculate your macros: Next, it’s time to set goals. What do you want to accomplish with keto? The more specific, the better. For example, your goal may be to achieve a certain weight or to get off of some of your diabetes medications. Also, be sure to calculate your personal keto macros and decide if you’ll be counting total carbs or net carbs.
- Prep your pantry: Next, get ready to start keto by stocking your pantry, fridge, and freezer with keto-friendly foods. If you’re able to, it’s also a good idea to get rid of high-carb foods so that they aren’t tempting you every time you enter the kitchen.
- Plan your meals: Before you start, make a plan for the next week. What are you going to eat, when? How will you stick to keto if you decide to eat out at a restaurant, if you get invited to a party, or if you get stuck working late? Thinking through these scenarios before they happen is key for success. As you continue, it’s a great idea to do a weekly meal planning session to keep yourself on track.
- Track your progress: Finally, you’ll need a good way to track your progress. This doesn’t necessarily have to be your weight, unless weight loss is your goal. You could choose to track your waist circumference, ketone levels, blood sugar levels, or more — it all depends on your “why” for doing keto.
Common Keto Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Below are some of the most common keto mistakes, along with some troubleshooting advice.
Too Many Carbs
On a very low-carb diet like keto, it’s shockingly easy to breeze past your daily carb limit. This is especially true if you’re not measuring your portion sizes or tracking what you eat in a food journal or app.
Here are three strategies to help you stop overdoing it on carbs:
- Check labels: Be sure to check the label of all packaged foods that you eat, or refer to a food tracking app to check carb counts. Some foods can be deceptively high in carbs, especially things like dressings, condiments, sauces, and gravies.
- Measure portion sizes: You also want to make sure that you’re measuring portion sizes. Research shows that we are all pretty bad at estimating portion sizes, which could lead to struggles on keto. The most reliable way to measure portion sizes is to use a food scale.
- Keep a food log: Finally, you’ll also want to track what you eat and drink — every bite. It’s easy to forget or gloss over snacks or a few stray bites of something, but these can add up quickly and drastically impact your daily carb count. Be sure to record everything.
Too Much Fat
Although keto is a high-fat diet, eating too much fat can hinder your weight loss goals. Although your body becomes better at burning fat when you’re in ketosis, it will always prioritize dietary fat over stored body fat if dietary fat is available.
Therefore, if you find that you’re not losing weight at the pace you want, it’s a good idea to cut back on the fat.
Not Enough Protein
Protein is essential for maintaining your muscle mass, and it helps keep you full too. If you’re getting hungry on keto, you may not be including enough protein (*).
At a minimum, you should strive to include 20-30 grams of protein — or a palm-sized (roughly four-ounce) serving of meat — with every meal and snack you have.
Ketogenic Diet Side Effects and How to Minimize Them
For many people, following keto is safe and side effect-free. Still, it’s important to be aware of the “keto flu” when you first start.
Keto flu isn’t an official condition, nor is it an actual flu. It’s a nickname that’s formed in the keto community for a collection of symptoms that are common when your body is adjusting to keto for the first time. These include:
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Headaches
- Muscle cramps
These symptoms are thought to occur due to electrolyte imbalances. When you enter ketosis, you lose a lot of water weight. As you lose this water, your body flushes out electrolytes too (* , *).
To help prevent keto flu, be sure to drink plenty of water (many people recommend one gallon per day) and supplement with electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
Risks and Precautions Before Starting the Keto Diet
Although keto is safe for many people, there are some things to consider before you get started — especially if you fall into any of the following categories:
- You have a diagnosed medical condition: Keto can affect your blood sugar, blood pressure, and brain function. Therefore, if you have any conditions related to these (such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or epilepsy), you should consult your healthcare provider before you start the diet.
- You’re pregnant or nursing: During pregnancy or nursing, it may be more difficult and risky to follow a keto diet. A better option may be a whole food based, minimally processed diet that includes healthy carbs, like paleo.
- You’re highly active: If you’re highly active and you switch suddenly to keto, you’ll probably experience fatigue and drops in performance initially. In this case, it may be a great idea to connect with a personal trainer or registered dietitian who specializes in keto diets and athletic performance (*).
- You’re taking prescription medications: Keto may also affect your medications. For example, the diet can lower your blood sugar and blood pressure levels, but if you’re also taking blood sugar- or blood pressure-lowering medications, this could be dangerous. Your doctor needs to be aware of your plans to start keto, so they can make adjustments to your medications as needed.
Remember: when in doubt, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider before you start keto. It can powerfully affect your health, so it’s important that you don’t rush into keto if any of the above points apply to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is keto safe?
For many people, keto is safe. Still, you should be aware of the “keto flu,” which can occur because of electrolyte and fluid balance shifts when you start the diet. Drinking plenty of water and supplementing with electrolytes can help prevent keto flu (* , *).
Also, if you’re highly active, taking prescription medications, pregnant, or nursing, you should consult a healthcare provider before you start keto.
How much weight can I expect to lose on keto?
This depends heavily on a few factors, including how much weight you need to lose, and how much of a calorie deficit you are in.
To lose weight, you need to consume fewer calories than you’re burning each day, even on keto. The best way to do this is to both slightly limit how many calories you eat and do more calorie-burning exercise. Strength training can also help you build muscle, which burns more calories at rest (*).
How to know if I’m in ketosis?
There are a few different ways you can check to see if you are in ketosis:
- Urine ketone strips: These strips are simple and inexpensive. They measure the ketones in your urine. They are helpful when you are first starting keto, but over time your body will become more efficient at burning ketones and there will be fewer in your urine — even if you’re in ketosis.
- Breath ketone test: A breath ketone test measures the ketones in your breath. Like urine tests, it’s more reliable for people who are new to keto.
- Blood ketone test: A blood ketone test is the most reliable for everyone, but also the most expensive. You will need a blood ketone meter as well as ketone testing strips made specifically for that meter.
What is the difference between keto and low carb?
“Low carb” is a general term that describes all diets containing roughly 130 grams of carbs or less daily, including keto. However, not all low-carb diets are keto — only those that are low enough in carbs to promote ketosis (*).
Some low-carb diets still contain too many carbs for you to be able to shift into ketosis.
How long should I be on a keto diet?
This is up to you. Many people report successfully following a keto diet for years and years. Other people choose to stay keto until they meet their health goals, then transition into something less restrictive.
The Bottom Line
Keto is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has provided amazing weight loss and metabolic health results for many.
But before you get started, you need to have a good idea of what you can and can’t eat, the potential risks of keto, and the basics of how it works.
Consider this beginner’s guide your go-to resource for getting started with keto.
