A huge challenge when going on keto is giving up traditional wheat-based or grain-based flours found in most traditional desserts.
Because, unfortunately, these flours contain a lot of carbs, which easily kick you out of ketosis. For example, one cup of all-purpose flour (made from hard and soft wheat) has 92 grams of net carbs (*)
When you’re on the keto diet, you need flour alternatives that are much lower in carbs. That way, you can still bake and cook some of your favorite recipes. Only this time, they’re better for your body.
You’ve probably heard of lupin flour as it has become more popular in the keto community — among other options like almond flour and coconut flour.
So, is lupin flour keto? What is lupin flour made of? Here’s more about this type of flour and its health benefits.
What is Lupin Flour?
Lupin flour is a low-carb flour that’s made from lupin beans (also called lupine or lupini). These are mustard-colored beans that date back before Ancient Rome (*). They’re native to the Mediterranean, North Africa, and Latin America.
While there are many species of lupins, the white lupin bean (Lupinus albus) is more common and has the most benefits (*). Interesting fact: The species L. mutabilis is considered one of the lost crops of the Incas (*).
Furthermore, lupin flour is suitable for baking and it can be used in a wide variety of gluten-free and grain-free recipes and products like low-carb pasta, biscuits, tortillas, noodles, bread, cakes, and cookies.
In fact, we’ve used lupin flour to make our Perfect Keto Mac & Cheese — the world’s first keto-certified pasta. If you’re on a gluten-free diet and trying to lower your carb intake, foods made using lupin flour are healthy options for you.
Another compelling fact about lupin flour is that it’s low in anti-nutrients like trypsin inhibitors and saponins compared to other legumes (such as soybeans and chickpeas) (*). In case you don’t know what anti-nutrients are, they’re plant compounds that limit your body’s ability to absorb important nutrients from food.

Is Lupin Flour OK for Keto?
Yes, lupin flour is a keto-friendly staple and can replace high-carb all-purpose flour. It may also be used as a substitute for keto nut flours like almond flour to further lower your carb intake (since lupin flour has fewer carbs than almond flour per serving).
When making keto recipes, you can choose to use lupin flour by itself or combine it with other keto flour options.
You may find it beneficial to experiment with recipes if you’re using lupin flour for the first time. One of the reasons is that some varieties taste slightly bitter. Neutralizing this may require adding sweeteners (like monk fruit) or seasonings.
How Many Carbs Are in Lupin Flour?
A ¼ cup (or 30 grams) serving of lupin flour has only 1 gram of net carbs. In addition, it contains (*):
- 11 grams of fiber
- 12 grams of protein
- 2 grams of fat
- 74 calories
Notice that on top of being so low in carbs, lupin flour is high in protein — even higher than almond flour and coconut flour, which have around 6 grams and 4 grams of protein, respectively (*). Those who are trying to optimize their protein intake while on keto may consume lupin flour as a plant-based protein source.
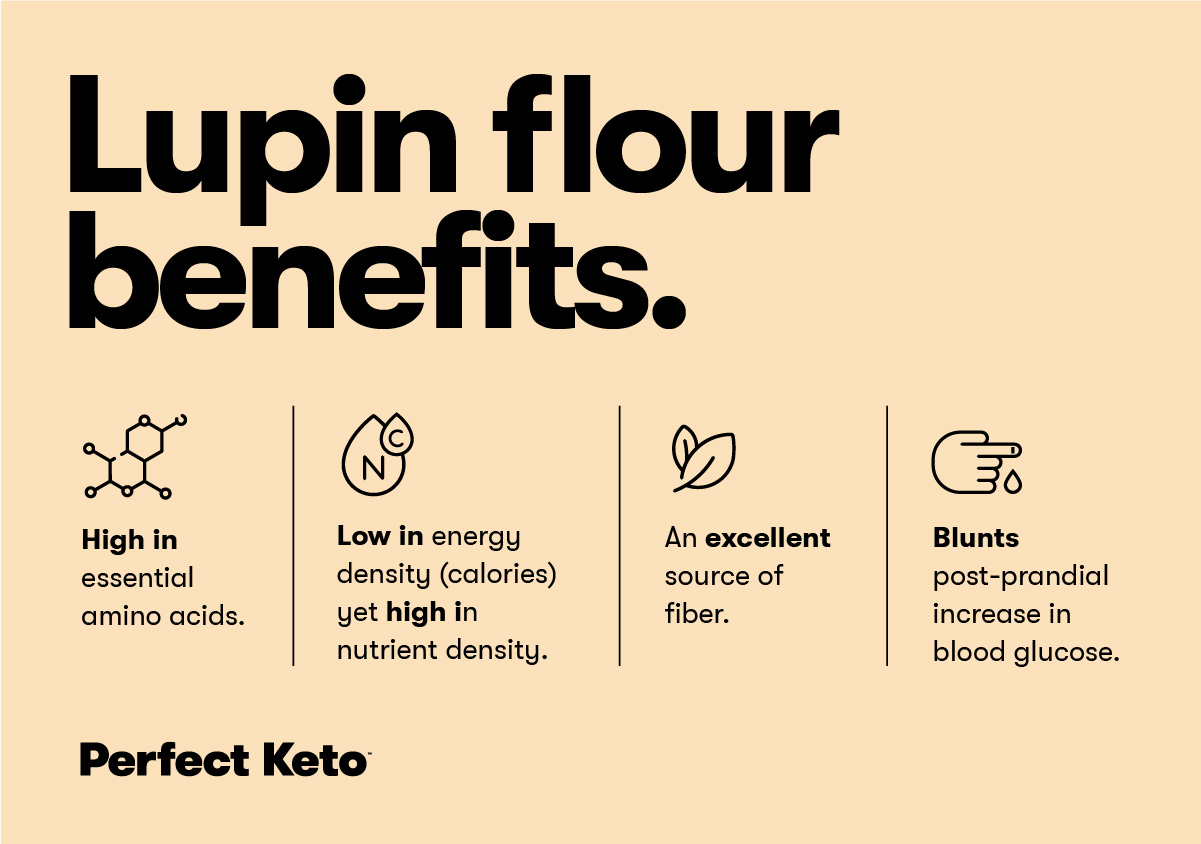
Lupin Flour Benefits
There are plenty of reasons why lupin flour makes a healthy addition to your low-carb diet if you’re considering it. Its benefits include:
Quality Protein Source
Providing 12 grams of protein per serving (¼ cup), lupin flour is rich in protein. It’s high in essential amino acids, which are protein molecules that your body alone can’t produce (*).
Furthermore, a research article in the British Journal of Nutrition mentioned that lupin protein is highly bioavailable (*). The term “bioavailable” means that your body can effectively absorb and utilize lupin protein since lupin is low in antinutrient compounds, as mentioned earlier in this article.
High in Fiber
In addition to being high-protein, lupin flour is full of fiber. Getting enough fiber can be challenging if you’ve just transitioned to the keto diet from a typical high-carb diet (since carb-rich foods contain plant-based ingredients, and plants are a source of fiber).
Dietary fiber helps promote bowel movements, increase satiety, and support weight loss (*). According to a review article, fiber expands the population of bacteria in your gut. In other words, it increases microbiome richness and diversity (*).
Unless you’re intentionally cutting out plants from your diet (to avoid antinutrients and address some digestive issues), lupin flour is a superior fiber source.
Nutrient-Dense
Lupin flour isn’t just low in calories, but it’s also surprisingly high in nutrients. Nutrients found in lupin flour include vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), phosphorus, potassium, calcium, iron, and zinc (*).
These vitamins and minerals help with important functions, such as energy production, fat metabolism, cell maintenance and repair, hormone production, and immune function.
Has Anti-Diabetic Effects
Consuming products made with lupin flour may benefit people who have (or are at risk for) diabetes.
In a randomized cross-over trial comparing the glycemic effects of whey protein and lupin protein, results found that both can control the increase of blood glucose after a meal. However, between whey and lupin, lupin led to a much lower insulin response (*).
Another study examined the effect of adding Australian sweet lupin flour to standard white bread. Blood samples were taken after fasting and many times after two hours of eating the meal. Results showed that lupin flour reduced the glycemic index (how quickly a certain food raises blood sugar levels) of the white bread (*).
Is Lupin Flour Better Than Other Keto Flours?
It depends on what your specific goals are. In terms of keeping carbs as low as possible and boosting protein intake, lupin flour is the superior choice.
To help you further, we’ve made a table comparing the nutrient profiles, uses, taste, and texture of lupin flour versus almond flour and coconut flour.
| Lupin Flour (¼ cup) | Almond Flour (¼ cup) | Coconut Flour (¼ cup) | |
| Net carbs | 1 gram | 2.4 grams | 6 grams |
| Protein | 12 grams | 5.8 grams | 4 grams |
| Fat | 2 grams | 14.1 grams | 3 grams |
| Fiber | 11 grams | 3 grams | 10 grams |
| Calories | 74 | 160 | 120 |
| Uses/Recipes | A wide variety of products and recipes (pasta, pastries like cakes, cookies, biscuits, etc.) | A wide variety of products and recipes (pasta, pastries like cakes, cookies, biscuits, etc.) | A wide variety of products and recipes (pasta, pastries like cakes, cookies, biscuits, etc.) |
| Taste | Neutral and somewhat starchy. Some people find that using 100% lupin flour in a recipe can cause a bitter aftertaste. Mixing it with other nut flours helps. | Mildly sweet and nutty. Those who are used to eating baked goods made with all-purpose flour will easily notice the nutty flavor of almond flour. | It has a distinct “coconutty” taste and aroma. If you dislike coconut, adding some spices and flavors helps to neutralize the taste. |
| Texture | Fluffy, airy, and less dense than other keto flours. Its texture mimics standard wheat flour. | It has a finer texture compared to almond meal. (Almond meal is sometimes used as a gluten-free substitute for bread crumbs.) | It has a gritty texture, making it a “heavy” flour. Make sure to sift coconut flour before adding it to your recipes. |
| Gluten-free? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Either almond flour or coconut flour can also serve as a lupin flour substitute depending on whether you need more fat or what your recipe calls for.
But, overall, these flours are keto-friendly, gluten-free, and are great wheat flour alternatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out these answers to common questions on lupin flour:
What is lupin flour made of?
Lupin flour comes from lupin or lupini beans, which are legumes and belong to the same plant family as peanuts (*). Making lupin flour involves drying the beans and grinding them.
What does lupin flour taste like?
It has a neutral taste while also being a bit starchy. Some may find lupin flour quite bitter. In that case, mixing it with other flours or adding keto sweeteners or seasonings will help mask this taste.
Does lupin flour cause inflammation?
The answer is no. In fact, a research study suggests that lupins possess anti-inflammatory properties (*). Furthermore, an open-label intervention found that taking a beverage containing Lupinus angustifolius (a species of lupin) protein hydrolysates helps decrease your risk of atherosclerosis (*).
Yes, Lupin Flour is Keto-Friendly!
There are lots of keto-approved flour substitutes for your favorite recipes, and lupin flour is definitely one of them. It’s also a quality source of protein, fiber, and micronutrients like thiamine, riboflavin, and iron. Plus, it has a neutral flavor, making it a versatile recipe ingredient.
While lupin flour still contains antinutritional compounds (or antinutrients), these tend to be lower compared to other legumes and wheat grains. So, if you’re striving to minimize antinutrients in your diet, you have a better chance of doing so by choosing lupin flour.
Interested in trying keto food made with lupin flour to support your diet? Try our Keto Mac & Cheese available in yellow cheddar and white cheddar flavors.