If you’ve tried going keto in the past or are considering it now, you may be wondering if it’s the right eating strategy for you and if it’s a plan you can stick with long-term. Some people complain the traditional ketogenic diet is too restrictive, unsustainable, lacking fiber, and inclusive of too many unhealthy saturated fats (think: fast food burger patties, bacon, and pepperoni).
The modified keto diet, also known as keto 2.0, was created to address these concerns and give the traditional keto diet a bit of a facelift. It’s still a low-carbohydrate eating plan that promises health benefits, but it’s less restrictive than the standard keto diet (SKD).
So, how does the modified keto diet work?
In this article, we’ll cover what sets the modified keto diet apart from traditional keto, whether it works to get you into ketosis, and which foods to eat and avoid. We’ll also answer everyone’s #1 burning question: can it help you lose weight?
Keep reading for all you need to know to decide if the modified keto diet is right for you.
What is the Modified Keto Diet?
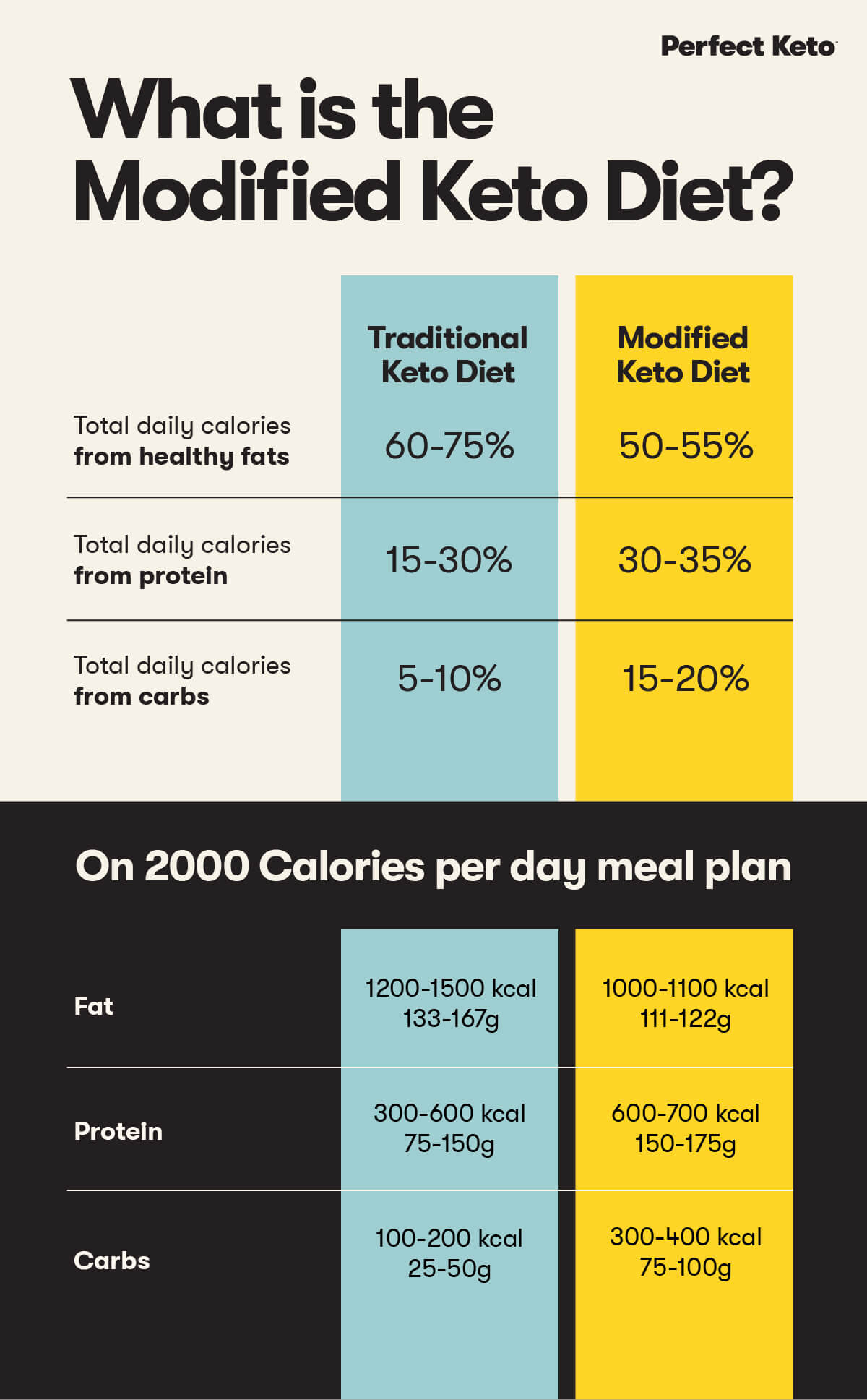
The modified keto diet is a low-carb eating plan that’s less restrictive than the traditional keto diet. Both diets are considered low-carbohydrate and high in fat, but they differ in how the daily macronutrients are divided.
The types of foods you eat don’t change much between the two diets — more on that soon — but how much of it you eat does.
The traditional ketogenic diet is defined by the following macronutrient guidelines:
- 60-75% of total daily calories come from healthy fats
- 15-30% of total daily calories come from protein
- 5-10% of total daily calories come from carbs
The modified keto diet doesn’t have defined macronutrient guidelines. However, the following breakdown is generally accepted as keto 2.0:
- 50-55% of total daily calories come from fat
- 30-35% of total daily calories come from protein
- 15-20% of total daily calories come from carbs
What do those percentages mean in real life?
Well, let’s consider a 2000 calorie per day meal plan.
On a traditional keto diet, 2000 calories would look like:
- 1200-1500 calories from fat or 133-167 grams of fat
- 300-600 calories from protein or 75-150 grams of protein
- 100-200 calories from carbs or 25-50 grams of carbs
On the modified keto diet, the same 2000 calories might look like:
- 1000-1100 calories from fat or 111-122 grams of fat
- 600-700 calories from protein or 150-175 grams of protein
- 300-400 calories from carbs or 75 to 100 grams of carbs
To sum it up, the modified keto diet allows you to eat significantly more carbs, slightly more protein, and less fat compared to a regular keto diet.
Remember that your daily calories and macronutrient breakdown will look different depending on body composition, physical activity, age, gender, and whether you want to lose, maintain or gain weight. A keto macro calculator can help you meet your goals.
If the idea of slashing your carb intake to next to nothing makes you second guess trying the standard keto diet, the modified keto diet might sound like a dream come true.
The modified keto diet claims it offers the same health benefits as the classic keto while allowing you to eat twice as many carbs.
How can that be? Can the modified keto diet help you achieve ketosis even with a higher daily carbohydrate allowance? Let’s take a closer look.
How Does the Modified Keto Diet Work?
The standard keto diet credits its health benefits, including weight loss, stable blood sugar levels, and fewer food cravings, to ketosis, which is when the body switches to burning ketones, sourced from fat, instead of glucose as its primary fuel.
Your body enters ketosis when glucose isn’t available from your diet and your glycogen stores have been depleted. The only way to remove glucose from the equation is to eat very few carbs.
For most people following ketogenic lifestyles, that means eating less than 50 grams of carbs per day. Anything more than that kicks most people out of ketosis and back to burning glucose for fuel.
So, if you can eat more carbs on the modified keto diet, can you still get into ketosis?
The truth is, it’s unlikely your body will reach ketosis on a modified keto diet. The macronutrient breakdown simply contains too many carbs for most people to reach and stay in ketosis.
This isn’t to say that some people following keto 2.0 won’t be able to get into ketosis, but it’s rare. Athletes and individuals with very active lifestyles may benefit from a slightly higher carb and calorie intake, while still maintaining ketosis and getting all its benefits.
Without ketosis, what’s so great about modified keto?
With more wiggle room for macros, the modified keto diet includes more plant-based fats and lean proteins, making it quite similar to the Mediterranean diet, which is considered a healthy diet that promotes longevity (*).
Keto 2.0 hasn’t officially been studied (and remember, there are no agreed-upon guidelines), but it can still offer the following health benefits:
- Promote weight loss. The modified keto diet can be a good way to change your eating habits, promote healthier food choices, and maybe even help you lose some stubborn body fat. Keep in mind if you don’t reach ketosis on the modified keto diet, weight may not come off as quickly as it tends to on standard keto.
- Increase satiety. A high-fat, low-carb diet can help you feel fuller for longer, which helps squash food cravings and aids weight loss.
- Support healthy blood sugar. Eating more fat and protein and fewer refined carbs, sugars, and starches can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Support heart health. Focusing on healthy fats, high-quality protein, and plenty of high-fiber, low-carb veggies can help keep triglycerides and cholesterol in check and minimize cardiovascular complications.
Modified Keto Diet Food List

The modified keto diet incorporates the following heart-healthy diet principles:
- Sourcing most of your dietary fat from plants
- Eating fewer servings of red meat and dairy
- Eating more fish
These guidelines help you eat more healthy, unsaturated fats and fewer saturated fats.
Foods to include on a modified keto meal plan include:
- Fatty fish – salmon, mackerel, albacore tuna, anchovies
- Meat – beef, pork, lamb, wild game
- Poultry – chicken, turkey
- Avocados
- Eggs
- Dairy – whole milk plain yogurt, full-fat milk
- Nuts – almonds, pecans, walnuts, cashews
- Seeds – flax, chia, sunflower, pumpkin, hemp, sesame
- Healthy cooking oils: Coconut oil, Avocado oil, Extra virgin olive oil, Ghee
- Low-starch veggies: Leafy greens (kale, spinach, swiss chard, collard greens), Zucchini, Eggplant, Asparagus, Bell peppers, Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, cabbage)
- Lower-sugar fruits: Berries (blackberries, blueberries, raspberries, strawberries), Citrus (lemons, limes, grapefruit, clementines), Coconut, Kiwi, Tomatoes
Depending on your unique macronutrient ratio and how many carbs you get from fruit, vegetables, and dairy, you may be able to include some higher carb foods from time to time such as:
- Higher sugar fruits – watermelon, cantaloupe, honeydew, bananas, peaches, and plums
- Higher starch vegetables – carrots, parsnips, sweet potatoes, winter squash,
- Sweet potatoes
- Legumes – beans, lentils
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Wild rice
Foods to Avoid in the Modified Keto Diet

You’ll limit or avoid the following foods on a modified keto meal plan:
- Refined grains – white bread, pasta, rice
- Most whole grains
- Most legumes
- Most starchy vegetables – white potatoes, corn, peas
- Breakfast cereals
- Snack foods – crackers, chips, pretzels
- Processed and cured meats – bacon, sausage, salami, lunch meats
- Sweeteners – table sugar, maple syrup, honey
- Sweets – cake, cookies, candy, pastries
- Fruit juice
- Sugar-sweetened drinks – soda, iced tea, energy drinks
- Alcohol
Takeaways
At first glance, the modified keto diet may seem like a healthier choice than standard keto. After all, keto 2.0 encourages you to eat more plant-sourced fats, healthy proteins, and plenty of leafy greens. You could almost call this approach a low-carb version of the Mediterranean diet.
If you’re not sure whether keto is for you, starting with a modified version might be a gentler way to initiate yourself to the high-fat, low-carb lifestyle.
The modified keto diet might help you adopt healthier eating habits and lose weight. However, the diet isn’t a true form of keto for most people.
Since modified keto includes more carbs than a traditional keto diet, it makes it more challenging to get into a state of ketosis.
Keep in mind that a traditional keto diet can also be well-balanced and filled with nutrient-rich foods. It gives you the best of both worlds: getting into ketosis and avoiding possible nutritional deficiencies while enjoying enhanced mental clarity, boosted energy levels, and optimal health.
Modified Keto Diet FAQs
What’s the difference between a modified keto diet and a standard keto diet?
The modified keto diet is more flexible and allows for more carbohydrates and protein and less fat than the standard keto diet. There’s no set amount for how much of each macro to eat on the modified version, but 50-55% fat, 30-35% protein, and 15-20% carbohydrate is a common breakdown.
Is a modified keto diet more sustainable than the standard keto diet?
Modified keto may be more sustainable for some people. A common complaint of the standard keto diet is it’s too restrictive. The modified version allows you to have a higher daily carb intake, so it can be a good choice for people who find standard keto restricts carb intake too much and individuals with very active lifestyles.
Will the modified keto diet help me lose weight faster?
A modified keto diet can still result in weight loss, but it’s unlikely to take the pounds off faster than a standard keto diet. Ketosis results in rapid weight loss, but it’s hard to reach and maintain when eating more carbs.
What are the benefits of a modified keto diet over standard keto?
Because the modified keto diet allows more wiggle room with carbs and lean proteins, you’ll likely find more options to eat at restaurants and social situations than you can when you’re following standard keto. Plus, the more flexible macronutrient breakdown may let you eat some healthy carb sources, like sweet potatoes or quinoa, from time to time.
Is the modified keto diet cheaper than standard keto?
Your grocery bill won’t differ much between modified and standard keto. Both diets focus on many of the same foods: healthy cooking oils, leafy greens, non-starchy veggies, berries, nuts, seeds, and avocados. High-quality meats and seafood, which are eaten on both diets, are pricier items.