Most post-workout foods aren’t keto-friendly. They have too much sugar, too little protein, too many additives — or all of the above.
Read the label of any popular pre-workout or post-workout bar or shake. Many of them are packed with grains, sugar, and additives.
Plenty of these bars contain your entire day’s carb allotment in one serving. All of them raise your blood sugar, kick you out of ketosis, and — worst of all — put you into fat-storage mode. No thanks.
Instead, you need post-workout foods that not only support your keto lifestyle — they support your fitness performance and recovery.
Unfortunately, most of the information about post-workout nutrition includes eating a ton of carbs after your gym session.
And that’s just not true.
In fact, muscle protein synthesis — or workout recovery — actually works better without carbs. Instead, you need plenty of protein and fat.
Get all the details in this article, including:
Before reviewing post-workout foods, however, you’ll want a primer on post-workout recovery. This knowledge will come in handy later.
Protein For Muscle Growth
When you lift weights, run, or dance-ersize, you break down muscle tissue. To come back stronger — to recover — that muscle tissue needs protein.
Specifically, those muscles need leucine — one of several branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) found in complete proteins. Leucine promotes muscle growth, or muscle protein synthesis[*].
Resistance exercise or strength training creates microscopic tears in your muscle tissue. This is perfectly normal, and it’s actually how your muscles grow. We’ll call that “muscle breakdown.”
When you eat adequate leucine-containing foods, you’ll maintain a positive net protein balance, and your muscles will grow back stronger.
Don’t eat enough leucine? The muscle stays broken down.
So how much leucine-rich protein should you eat?
That depends how much you exercise[*]:
- Heavy exercise: 1.6 g / protein per kg body weight
- Moderate exercise: 1.3 g / protein per kg body weight
- Not much exercise: 1 g / protein per kg body weight
Up to 2 g protein/kg body weight a day — about 160 grams protein for a 180-pound person — is considered safe[*].
And what about protein intake on a ketogenic diet? It turns out that moderate- to high- protein intake is fine — even when you’re keto. Although most people keep their protein intake to around 30% of caloric intake, it’s unlikely you’ll experience gluconeogenesis even if you eat more than that.
Use the Perfect Keto Calculator to see how your macros stack up, then adjust according to your activity level and goals.
Protein Timing
A brief word on protein timing and the post-workout anabolic window. You do need protein to build muscle — but it doesn’t matter if you eat that protein before or after the workout. The result will be similar[*].
Optimize Your Fitness Goals

Keto Whey Protein – Power Your Workouts & Accelerate Recovery. Ideal Protein Source for a Keto Lifestyle.
How The Keto Diet Preserves Muscle
A low-carb high-fat keto diet not only burns adipose tissue (body fat), it also preserves lean tissue.
Here’s how:
#1 Keto Spares Muscle
Ketones are your backup energy source. When you eat a low-carb high-fat diet, your body stops using glucose and starts using ketones.
When ketones enter your bloodstream, they send a message to your body: carbs are scarce — time to burn fat and preserve muscle. Technically speaking, ketones (specifically beta-hydroxybutyrate or BHB) interact with the amino acid leucine in your muscles to promote protein synthesis, aka muscle growth and repair[*].
This adaptation helped hunter-gatherers stay strong in times of famine.
As long as you have fatty acids and ketones in your bloodstream, your muscles will stay strong. Get adequate protein, and they’ll get even stronger.
Along with boosting BHB, keto also boosts adrenaline.
#2 Keto Boosts Adrenaline and Growth Factors
Going keto lowers blood sugar and low blood sugar stimulates adrenaline production. Adrenaline then increases both muscle preservation and fat loss[*].
In addition to adrenaline, low blood sugar also signals the release of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). These hormones interact with your muscle cells, telling them to grow and recover.
Now for some clinical trials on the muscle-sparing effect of keto.
#3 Keto Improves Body Composition
There’s plenty of evidence that keto improves body comp in overweight people[*]. But what about in healthy people?
To answer that question, researchers fed 26 athletic young men two diets: low-carb keto and a high-carb conventional western diet.
After 11 weeks of weight training, the keto athletes had more muscle — and less fat — than the high-carb athletes[*].
So for building muscle — where keto succeeds, high carb fails. You’re about to learn why.
Why Carbs Fail Your Muscles
You may have heard the rumor that you need carbs to build muscle. More specifically, that you need insulin. And nothing raises insulin better than carbs.
This is really old information, though.
Yes, insulin is technically an anabolic or “building” hormone, but it’s not true that you need it to build or maintain muscle.
The truth is: when you’re getting enough leucine, you need very little insulin to repair muscle[*].
For instance: in a small controlled study, a low-carb keto diet promoted muscle synthesis better than a high-carb western diet[*].
The consensus? You don’t need carbs for muscle growth. Plenty of protein and healthy fats will do.
But what exactly should you eat to maximize recovery and stay keto? Read on to find out.
The 10 Best Keto Workout Foods

#1 Whey Protein
The amino acid leucine is necessary for muscle growth. And whey protein is your ultimate source of leucine.
First of all, whey protein is a complete protein — meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids, including muscle-building branched chain amino acids. You can’t synthesize essential aminos like leucine. You have to get them through food or supplementation.
Compared to other protein powders, whey stacks up favorably. In fact: according to the World Health Organization (WHO), whey ranks higher for digestibility and efficiency than casein, hemp, pea, or soy protein[*].
And when it comes to post-workout recovery, whey is king. Two quick examples now.
In one study, researchers gave 12 athletes whey or carbs, then had them lift weights. Unsurprisingly, whey won. To be specific: at both 12 and 24 hours post-workout, the whey-supplemented group had better markers of muscle recovery, strength, and power[*].
Another study, this time on 70 older women. After 12 weeks of strength training plus either a whey or placebo pre- or post-workout, the whey-supplemented women stayed stronger[*].
They also maintained more muscle mass than placebo control — a promising victory in the fight against age-related muscle decline.
Whey also pairs nicely with keto-induced weight loss. For instance: one group of researchers showed that adding whey to a ketogenic diet preserves muscle and blasts fat[*].
Whey protein isolate — preferably the grass-fed variety — is easy to add to your keto lifestyle. Just scoop 20-30 grams into your smoothie and blend away.
#2 Meat And Fish
Both high-quality grass-fed, pastured meat and wild-caught fish are excellent sources of fat and protein. Because of this, both make a great post-workout meal.
Meat and fish, like whey, are complete proteins. Remember: you can only get leucine from complete proteins.
Plus, both meat and fish are super keto-friendly — especially the fattier choices like wild-caught salmon or a nice grass-fed rib eye.
For reference, the keto diet is about 60% fat, 30% protein, and 10% carbs by calories[*]. A salmon fillet is fatty and protein-rich, making it the perfect post-workout meal. Plus, it won’t add to your carb quota.
In addition to protein and fat, salmon also contains the omega-3 fats EPA and DHA. Omega-3s are anti-inflammatory and have been shown to minimize post-workout soreness[*].
A final benefit of meat and fish? They tend to be hypoallergenic.
Some people can’t eat dairy — which rules out casein and (sometimes) whey. Others have trouble with soy. Others still with egg.
If any of these sound like you, perhaps meat and fish should be your post-workout protein source of choice.
Another hypoallergenic, gut-friendly choice? Collagen powder.
#3 Collagen Powder
When you work out, you don’t just break down down muscle. You also break down connective tissue.
Connective tissue holds your bones together, determines your force output, and influences your range of motion[*].
What’s that connective tissue made of? It’s made of collagen. And so after exercise, collagen synthesis is crucial for recovery.
And the best way to boost collagen synthesis is to consume collagen powder[*].
Collagen powder doesn’t contain much leucine, but it does contain high amounts of the amino acids glycine and proline. These aminos are your chieftains of collagen production.
Is collagen keto, you ask? Yes indeed — collagen is the perfect keto food.
That’s because collagen doesn’t add to your carb count and helps keep your blood sugar low[*]. And low blood sugar is how your body knows to stay in ketogenic, fat-burning mode.
#4 Eggs
The egg is nature’s ketogenic miracle: high fat, moderate protein, very low carb.
According to the WHO, egg protein is the only protein that rivals whey for efficiency, bioavailability, and digestibility[*]. Which means that eggs — like whey — are a great choice to support your body post-workout.
Egg yolks are also high in choline, a nutrient that powers mitochondria in muscle cells[*]. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of your cells, so this is great news for strength and recovery. No choline, no power.
And like salmon, pasture-raised and organic eggs contain anti-inflammatory omega-3s. Good for minimizing soreness after a workout.
Here’s the thing about eggs though. They take time to make. And if you want to buy a good-quality egg white protein, brace yourself for sticker shock.
Plus, a lot of people are sensitive or allergic to eggs, taking them off the table entirely.
Nonetheless, if you find yourself at a breakfast buffet and you can tolerate eggs — skip the croissants and load up on scrambles and omelets instead.
Or just have a protein bar.
#5 Protein Bars
It’s hard to find a keto-friendly protein bar. Most of them have way too many carbs. Even worse — those carbs often come from straight-up sugar.
Too many carbs spike your blood glucose, which raises your insulin levels, which slams the door on ketosis. And with high insulin levels — a fat storage hormone — you can’t lose fat.
Keeping your blood sugar low, on the other hand, keeps you in keto mode — and keto helps you lose weight, burn fat, and preserve muscle.
So yes, you want to stay in keto.
But you also want something quick after a workout. Something high in protein that won’t kick you out of ketosis. Something without artificial flavors, artificial colors, or sugar alcohols.
One option — maybe the only bona fide “keto-friendly” option — is the Perfect Keto Bar. With 10 grams of protein, 19 grams of fat, and 1 gram of sugar, this is a fantastic (and delicious) option for keto gym-goers.
Speaking of keto, how about drinking some ketones post-workout?
#6 Exogenous Ketones
When you eat a ketogenic diet, your body starts producing the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). In turn, BHB lowers your blood sugar and preserves muscle[*].
But diet alone isn’t the only way to increase your blood ketone levels. You can also consume ketones directly.
These edible ketones — called exogenous ketones — come in two forms: ketone salts and ketone esters. Ketone esters are more potent, but they don’t last as long as ketone salts[*]. Plus the esters taste kind of nasty.
And exogenous ketones can enhance exercise performance.
Researchers fed 10 athletes a carb-heavy drink, a fatty drink, or a ketone drink before a cycling session. After the workout, the ketone-fed athletes had[*]:
- Increased fat burning
- Improved glycogen conservation
- Lower muscle lactate levels (indicates better muscle endurance)
- Higher BHB levels
Another benefit of exogenous ketones? They help move blood sugar out of your blood and into lean body mass. In other words, you enhance athletic performance and lower your blood sugar at the same time.
And since high blood sugar is linked to obesity and chronic disease[*][*] — it’s good to keep it low.
Another way to boost ketone levels and lower blood sugar? MCT oil.
#7 MCT Oil
MCT oil — or medium chain triglyceride oil — is a type of fat derived from coconut oil. You’ve probably heard of it, maybe even had some.
The nice thing about MCT oil? Adding some to drinks or meals — even just a few grams — can get you into ketosis pretty quickly.
That’s because, unlike other fats, MCT oil heads straight to your liver for ketone conversion. MCT oil is your keto-shortcut — an easy hack to raise blood BHB levels[*].
And higher BHB levels, you just learned, synergize with leucine to preserve and repair muscle tissue.
Getting ketones and leucine together is simple. Just add MCT oil — or MCT oil powder — to your post-workout protein shake.
Another food to add to that shake? Think green.
#8 Greens
Your macronutrient requirements on keto are simple enough — fat, protein, carbs. You already know the best ratios.
Micronutrients, however, are not so simple. You need dozens of nutrients for everything from brain health to respiration to workout recovery. Vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin C, magnesium, iron, zinc, iodine — the list goes on.
To get your micronutrients — Grandma was right — you need to eat your vegetables. Especially your greens.
But even if you follow Grandma’s advice, you may still be short on micronutrients. You’d need to eat 3-4 cups of spinach, for instance, to reach your daily requirement for magnesium[*].
When it comes to building muscles — and supporting your nervous system — magnesium is a non-negotiable[*]. Without enough magnesium, you simply can’t perform.
Next time you make a post-workout shake, consider adding a well-formulated greens powder to the mix. That way, you’ll cover your macro and micro requirements all in one shot.
Next, another macro/micro powerhouse: the avocado.
#9 Avocado
One cup of avocado contains the following macronutrients[*]:
- 22 grams fat
- 4 grams protein
- 13 grams carbohydrate
Wait, isn’t 13 grams of carbs too high?
Not in the presence of dietary fiber. The thing is, an avocado has 10 grams of fiber — and this fiber offsets the carb load by limiting your blood sugar response.
To put it mathematically: 13 grams carbs – 10 grams fiber = 3 grams net carbs.
And so, for your keto purposes, you only need to count 3 grams of carbs from an avocado. Phew.
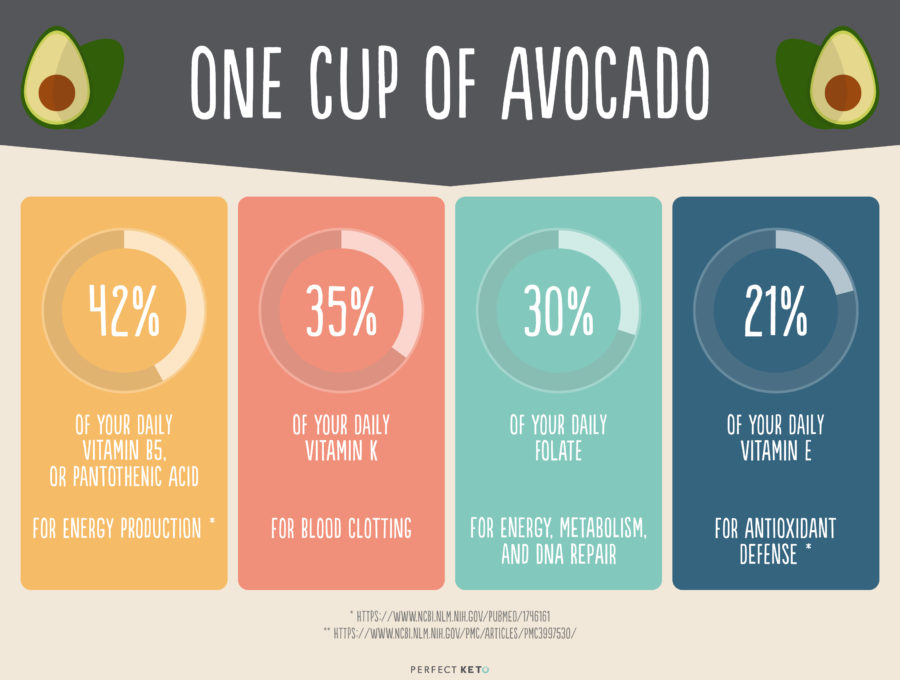
Avocados are strong in the micronutrient department too. In just one cup of this green fruit, you have:
- 42% of your daily vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid — for energy production[*]
- 35% of your daily vitamin K — for blood clotting
- 30% of your daily folate — for energy, metabolism, and DNA repair
- 21% of your daily vitamin E — for antioxidant defense[*]
Finally, texture. Avocados turn your smoothie from runny mess to thick, velvety pudding. Yum.
If you’re still hungry after that smoothie, consider a handful of nuts.
#10 Nuts
Want to add more fat to your diet without chugging olive oil?
Easy. Eat nuts.
Almonds, macadamia nuts, cashews, walnuts, and pistachios are all high fat, low carb, keto-friendly snacks.
But nuts aren’t just good sources of macronutrients. They’re also good sources of micronutrients.
A quarter cup of walnuts, for example, contains 53% of your daily copper, 44% of your daily manganese, and 20% of your molybdenum[*].
Take copper. It’s crucial for collagen synthesis — which, as you learned, is part of any good workout recovery[*]. And it’s hard to get enough copper through diet.
So if you live a keto lifestyle, nuts should be a mainstay in your snack routine. Nothing’s easier to bring to the gym, office, or movie theater.
If you want to mix it up, consider nut butter — the delicious, semi-liquid form of nuts. It beats the pants off chugging olive oil.
Now that you’ve loaded up on the best post-workout keto foods, it’s time to put your keto workout plan into action.
Keto-Friendly Workout Tips

#1 Limit Carbs
You do not need carbs to build muscle.
In fact, eating carbs will impede your keto workout goals.
With that in mind, try this strategy. Calculate your daily carb intake, then write that number down.
If that number is over 10-15% of your total caloric intake, you may be out of the keto-zone.
To bring your carb intake down, make some swaps. Swap nut butter for jelly, avocado for banana, Keto Bars for other higher-carb bars.
Soon you’ll be fueling your workouts like a ketogenic champ — and your muscles will thank you.
#2 Blend A Post Workout Smoothie
You can almost every item on today’s list to a post-workout smoothie. Here’s what that smoothie might look like:
- 20-30 grams grass-fed whey protein isolate
- 1-2 tablespoons MCT oil powder
- 1 scoop exogenous ketone salts
- 1 medium avocado
- 2-3 scoops collagen protein powder
- 1 scoop greens powder
- ½ cup coconut milk
This smoothie is high fat for your keto goals and high protein for your muscle synthesis goals. Plus it has a ton of micronutrients.
The best part of having a smoothie routine? It spares you the agony of decision fatigue.
#3 Snack Wisely
Even if you go keto and cut your cravings, you’ll still want a snack now and then. That’s okay.
What’s not okay is snacking on junk food — chips, high carb protein bars, cookies, etc. These foods will boot you out of ketosis and make your cravings even worse.
Instead, you need to arm yourself with high-fat snacks — keto bars, nuts, nut butter, and coconut chips — that stave off hunger, fuel exercise, and keep you in fat-burning mode.
Think of it as a pantry makeover. You can do it.
#4 Exercise Right
When it comes to staying strong and looking good, proper nutrition is only half the equation. The other half, of course, is exercise.
Here are some movements to help you stay lean, mean, and healthy:
- Bodyweight exercises like squats, push ups, pull ups, or planks
- Heavy lifts like back squats, deadlifts, bench press, or kettlebell swings
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) — shown to boost hormones associated with muscle growth[*]
- Yoga — useful for strength, mobility, and flexibility
- Walking
Your exercise options are nearly limitless. Pick a few, cycle high- and low-intensity, build in recovery time, and reap the benefits.
Post Workout Keto Fuel
Picture this. You finish your workout, feel famished, and walk to your gym’s food counter.
The options are usually bleak. The protein bars are more like candy bars. The protein shakes are more like milkshakes. High-carb, high-sugar nightmares.
You can wait a few minutes until you get home.
There you have all the ingredients to make the perfect keto smoothie. Whey protein, MCT oil powder, collagen, avocado, greens powder, nut butter — perfect for post-workout fuel.
It will be a high-fat, high-protein keto bomb designed to enhance your recovery. And it will hit the spot.
