When we’re physically wounded, our bodies respond immediately to try and heal the damaged area. However, if proper nutrition is lacking or there’s too much inflammation, healing can be affected.
Many of us know that what we eat has an impact on how we feel and how our bodies function. Wound healing is no exception here. By following a healthy low-carb ketogenic diet, there are some special benefits of ketosis for wound healing. We’ll be looking at those benefits here.
What Affects Wound Healing?
When it comes to wounds, there are several factors that can affect the body’s healing efficiency, including age, vitamin deficiencies (more on that below), and low protein intake. However, the number one factor is diabetes. [*]
Diabetics often experience slower wound healing due from unbalanced blood sugar levels, and here’s why (and why it matters):
High blood sugar levels can impede the body’s healing response and cause cell walls become rigid and stiff, making it harder for blood to flow through the small blood vessels at the wound’s surface needed to create new skin tissue.
Excess glucose contributes to extra inflammation in the body, which can impede the healing process.
This shows the strong relationship between glucose levels, inflammation, and healing. By putting the body into ketosis, burning fat for fuel instead of glucose, we can help prevent excess levels of glucose in the body.
Inflammation and Ketosis for Wound Healing
Now, it’s important to note that inflammation is good and normal in regular amounts. In fact, our bodies respond to damage by temporarily dilating the blood vessels. This causes the wound area to get red, warm, and swollen as pathogens are killed off and protection is built so the wound can heal.
In this respect, inflammation is the body’s good built-in defense against disease. However, the degree of inflammation matters. If we’re walking around with inflamed bodies all the time, often a result of excess glucose levels, problems will arise because there’s nothing to counter the response.
Stress and Wound Healing
Another factor that encourages inflammation and slows wound healing is stress.[*]
Besides finding ways to manage day-to-day stress, avoiding too much caffeine, and getting enough sleep, managing blood sugar has a big influence on how much the stress hormone cortisol is made. So, if we’re eating a lot of sugars and other carbohydrates, it can increase cortisol levels, thus increasing inflammation.
Bottom line, when inflammation remains present, it makes it more difficult for things to heal. Eating low amounts of sugars and carbs foods and increasing anti-inflammatory foods, like those present on a ketogenic diet, is a great way to help improve healing over time.
Blood Flow and Healing
Being in ketosis might also benefit healing by providing an alternative energy source to glucose and improving blood flow. []] Maximum blood flow to a wound is important for the clotting and healing process.
Ketogenic Nutrition for Wound Healing
The nutrient ratios of the ketogenic diet can be great for promoting efficient wound healing:
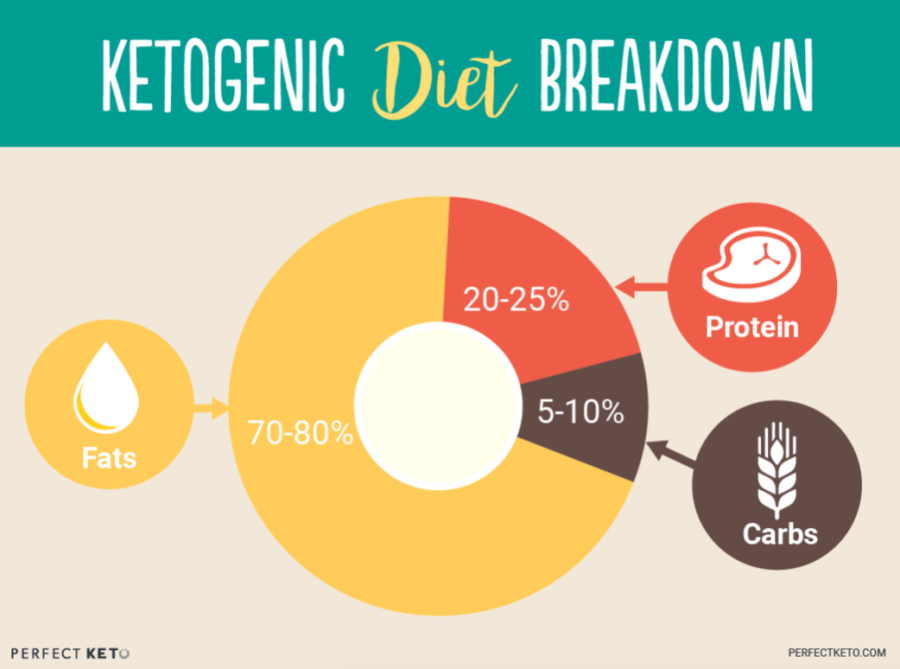
The high intake of good fats, especially omega 3s, from the ketogenic diet are important for healing cell membranes and reducing the inflammation that can prevent wound healing.
Intake of high-glycemic, processed foods like omega 6 fats from corn and soybean oil, sugars, and refined carbohydrates can increase insulin levels in the body and encourage a constant low-grade inflammation that isn’t conducive to proper healing. Thankfully, these foods aren’t present on a ketogenic diet and while in ketosis.
Protein is also an important nutrient for wound healing. The moderate intake of protein on the ketogenic diet allows the body to still remain in ketosis without breaking down proteins for energy, so they can go their job in helping heal the wound.
Nutrients that Help Wound Healing
An overall nutritious diet is important, but there are specific nutrients that the body needs specifically to heal. Thankfully, each are easy to obtain while in ketosis and eating ketogenic diet foods. Here are the key nutrients and where you can get them:
- Vitamin C: Eat fresh low-carb vegetables: dark leafy greens like broccoli, spinach, and kale, and bell peppers. The body needs vitamin C to make collagen.
- Protein: The ketogenic diet includes a moderate intake of protein from high-quality sources: meats, eggs, nuts and seeds, and sometimes full-fat dairy.
- Zinc: Getting enough zinc is no problem on a balanced ketogenic diet, as meats, seafoods, and many nuts are rich in zinc.
- Vitamin K2: Eat leafy green vegetables and fermented foods. Grains are off the table for keto, so if you aren’t eating enough vegetables or fermented foods (which are really important — if you haven’t added them to your diet yet, we recommend you do), you might want to supplement with K2.
- Vitamin A: Found in liver, butter, eggs, and leafy greens like broccoli, kale, and spinach. You can also get vitamin A by supplementing with cod liver oil.
- Vitamin D3: Found in sardines, salmon, tuna, and raw milk. High enough levels of vitamin D3 can help ensure the body’s immune system is able to operate effectively, which is important for healing wounds efficiently.
Overall, inflammation in the body can interfere with many different daily functions and that includes the healing of wounds. Our bodies are fighting for us 24/7. By eating a low-glycemic, ketogenic diet, we can help reduce excess inflammation and stress on our bodies, feed them plenty of anti-inflammatory fatty acids, and assist them in healing as efficiently as possible.