Keto and Atkins are two popular low-carb diets.
Both keto and Atkins share a central idea: you can improve your health by limiting your carb intake — cutting out high-carb food groups like whole grains, carb-heavy processed foods, starchy vegetables like potatoes, and desserts.
If you’re new to low-carb diets, these two diets may look quite similar. But while there are some similarities between them, there are also a few key differences that set them apart from one another.
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
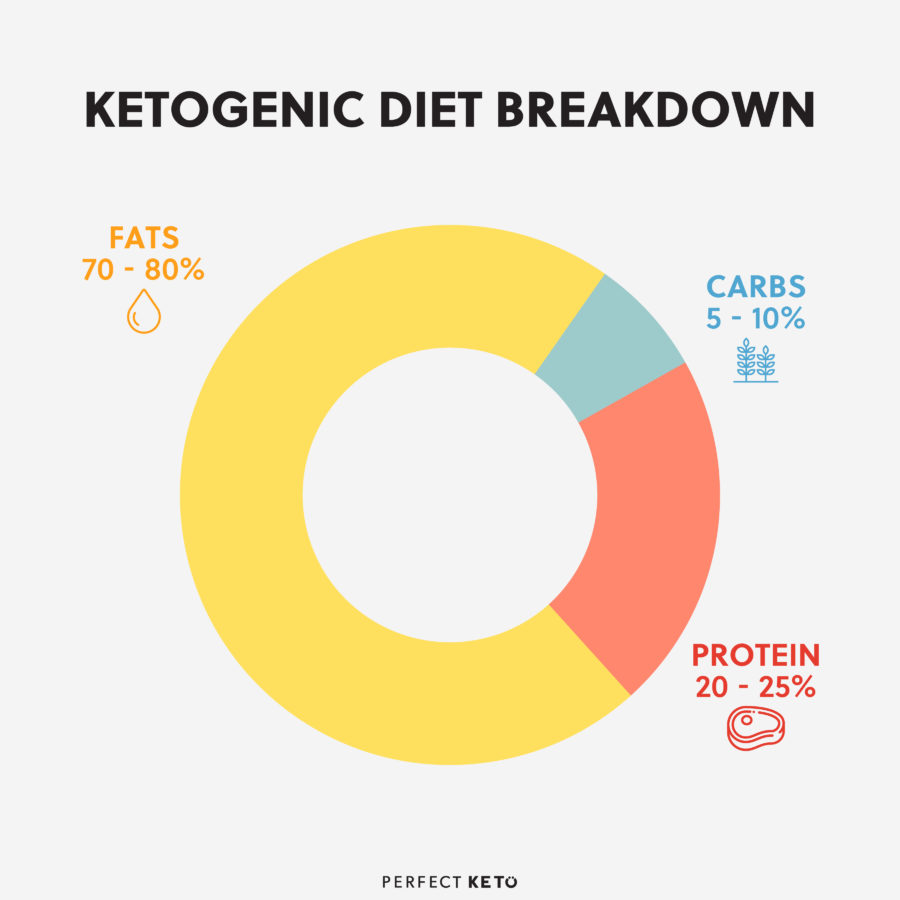
The keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, moderate-protein, high-fat diet plan.
The goal of keto is to get your body into ketosis, a metabolic state in which you burn primarily fat for fuel, instead of sugar or carbs.
When you’re in ketosis, your body runs on ketones, little bundles of energy that come from either the fat you eat or your stored body fat.
Ketosis comes with a wide variety of health benefits, including weight loss, stable blood sugar, and better brain function.
In order to get into ketosis, most people have to eat under 50g of net carbs (total carbs minus fiber) a day. A typical macronutrient breakdown for keto is:
-
-
- 75% fat
- 20% protein
- 5% carbs
-
What is the Atkins Diet?
The Atkins diet is also a low-carb diet, but it works a little differently than keto does.
Atkins is broken down into four phases geared toward weight loss. You set yourself a goal weight, then move through four phases, depending on how much weight you lose:
- Induction Phase. During this first phase, you eat under 20 grams of net carbs a day, until you’re within 15 pounds of your weight loss goal. You’ll almost certainly be in ketosis during this phase of Atkins.
- Phase 2. You increase your carb intake to 25-50 grams of net carbs a day until you’re within 10 pounds of your goal weight.
- Phase 3. To lose the last 10 pounds, you increase your carb intake to 50-80 grams of net carbs a day, until you hit your weight loss goal and maintain your goal weight for one month.
- Phase 4. Once you’ve stayed at your goal weight for a month, you can eat up to 100 grams of net carbs a day. You stick to phase 4 indefinitely to maintain your weight loss.
With Atkins, you gradually increase your carb allowance as you lose weight.
Keto Vs. Atkins: Similarities and Differences

Keto and Atkins are similar in some ways, but they also have key differences that lead to significant changes in how they affect your health and weight loss goals.
Similarities
Keto and Atkins overlap in a few different ways. For once, they’re both low-carbohydrate diets that emphasize high fat intake and moderate protein intake.
In fact, the induction phase and phase 2 of the Atkins eating plan are nearly identical to keto. In those two phases, you’re limiting your net carbs to under 50 grams a day (~5% of your daily calories), which should put you into a state of ketosis.
Both diets focus on eating moderate protein and higher fat, and they’re both centered around avoiding carbs, especially refined carbs and sugar.
Keto and Atkins also have strong research showing that they’re good for losing weight. They both outperformed higher-carb diets in studies looking at sustainable, long-term weight loss[*][*].
Differences
The main difference between keto and Atkins is that a ketogenic diet keeps you in ketosis all the time.
On Atkins, you’re likely in ketosis for the first two phases (you may see these phases called Atkins 20 and Atkins 40). That means you’re burning primarily fat for fuel, not sugar and carbs.
But in phase three and the maintenance phase of Atkins, you will likely transition out of ketosis and simply eat a moderately low-carb diet.
Keto, on the other hand, is very low-carb all the time, which means your body is in a consistent state of ketosis.
Ketosis offers a few additional benefits that you may not get during the later stages of Atkins. However, some people find they do better with slightly higher carb intake, and that a non-keto low-carb diet like Atkins works better for their body.
Which diet is best depends on your unique nutritional needs.
The Benefits of Ketosis
If you feel good in ketosis, you may want to consider following a keto diet. Ketosis comes with a few benefits that you won’t get during the later stages of Atkins. Benefits of ketosis include:
Hunger Suppression
When you’re in ketosis, you burn fat as your main fuel source instead of sugar. Your body turns fat into ketones, little bundles of energy that power your cells.
Ketones are a great energy source, but they also help with dieting. They turn off ghrelin, your body’s main hunger hormone, which suppresses your appetite[*].
This is one reason there are so many keto success stories when it comes to weight loss (here, here, and here, for example). On a keto diet, you can stay in a mild calorie deficit and gradually, sustainably lose weight, without the constant hunger that you feel on other diets.
Faster Metabolism
People in ketosis also burn an average of about 300 extra calories a day, compared to people on a low-carb diet with macros similar to Atkins phase 3/4[*].
When you eat a ketogenic diet, you burn more calories and feel full on less food. That’s a great recipe for weight loss — but it doesn’t happen with higher carbohydrate intake, like on Atkins or a low-fat diet.
Keto’s extra calorie-burning benefits can also guard against weight gain when you stop trying to consciously lose weight.
Blood Sugar Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Management
Carb restriction, in general, is a good choice if you get blood sugar crashes or sugar cravings, or if you have type 2 diabetes. Limiting carbs and sugar keeps your blood sugar more stable, and keto and Atkins are both good for blood sugar control[*][*].
However, a ketogenic diet seems to be the best choice for managing blood sugar.
On keto, you eat so few carbs that your blood sugar remains consistently low and stable — to the point where many people with type 2 diabetes can get off their medication entirely[*][*].
Atkins also controls blood sugar and can help people reduce their type 2 diabetes medications, but in studies, it didn’t help people get off their medication entirely, the way keto can[*].
Improves Brain Health
Because ketones easily cross the blood-brain barrier, your brain can use them efficiently for energy, leading to sustained mental performance. Early research even suggests that a ketogenic diet may protect your brain against diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and overall neurodegeneration[*].
Ketones can do wonders for your mental health and brain function, including[*][*]:
-
-
- Preserving neurons and synapses, which improves short-term memory, focus, attention, and learning
- Lowering neuroinflammation
- Improving cognition in people with dementia
-
Again, these benefits are specific to a ketogenic diet.
Decreased Risk of Heart Disease
Your cardiologist might be happy if you switch to keto, too. Ketones have antioxidant effects on the lining of your blood vessels, improve blood circulation, and increase the efficiency of your heart.
Studies found the mechanical efficiency of the heart increased by 30% and blood flow increased by 75% when running on ketones[*][*][*].
Getting into a state of ketosis also reduces risk factors for heart disease, including lowering your triglyceride levels and increasing your “good” HDL cholesterol levels[*].
The Benefits of Atkins
On Atkins, you increase your carbohydrate intake, especially during the later phases of the diet.
Some people prefer the added flexibility that Atkins offers. Eating more carbs than a keto diet allows can be helpful in certain situations.
Athletic Performance
High-level athletes may benefit from slightly higher carb intake than you get on a keto diet, although research is mixed.
A recent study of super-endurance athletes found that people in ketosis and people eating carbs performed equally well during a three-hour run[*].
However, another study found that keto-adapted endurance athletes didn’t do as well without carbohydrates as fuel[*].
Anecdotal reports from people are similarly mixed. Some do just fine working out on keto, while others experience a decrease in performance.
If you’re a high-level athlete and your performance suffers on keto, Atkins is a good way to introduce more carbs into your diet.
You can also try variations of keto that are geared specifically toward athletes, like a cyclical keto diet or a targeted keto diet.
Thyroid Hormones
A ketogenic diet may decrease thyroid hormone production in some people[*] — although again, research is mixed.
The majority of people follow a keto diet without any thyroid issues, and some people with autoimmune thyroid issues actually report an improvement in their symptoms when they switch to keto.
Thyroid hormones regulate carbohydrate metabolism, and some keto experts theorize that the decrease in thyroid activity happens because on keto, your need to metabolize carbs drops significantly.
However, at present, this is purely a theory, and some people who try keto, especially women[*], may see a drop in thyroid hormone production that can cause fatigue and other health issues.
If you have a history of thyroid issues, talk to your doctor about starting a keto diet. If you need more carbs, Atkins may be a better choice for you.
Conclusion
Both keto and Atkins are similar diets, but the key difference that sets them apart is ketosis.
On a ketogenic diet, you’re in ketosis all the time, which comes with additional benefits to your overall health that you won’t necessarily see during the later stages of Atkins. Ketosis is particularly useful for weight loss, heart health, brain function, and blood sugar management.
However, constant ketosis isn’t for everyone. High-level athletes and people with thyroid disorders may do better on a higher-carb diet like Atkins. Or you may just feel better eating more carbs.
What matters most is finding a diet that’s sustainable for you long-term and the best way to figure out your ideal diet is to work with a nutritionist or a dietician and try a few different ones to see what works.